IDC anticipated that the global datasphere will reach 175 zettabytes by 2025 in its Data Age 2025 research for Seagate. According to the same study, by 2025, 6 billion individuals, or 75% of the world’s population, will interact with internet data on a regular basis. With this humongous amount of data that businesses and consumers are dealing with on a daily basis, the appetite for data analytics goes without a question. Companies are constantly seeking essential information from huge amounts of data generated, accessed, and stored in a variety of locations. The value of this data in important business decision-making is enormous. The ability of a company to obtain reliable data, understand it correctly, and act on those insights is critical to its success.
The understanding of data structure is the key to unlocking the value of such large amounts of data. Data is sourced, collected, and scaled in distinct ways for structured and unstructured data, and each is stored in a different database. Although some data is structured, the majority is unstructured. Unstructured data makes up the majority of data (about 80%). This means structured data accounts for only roughly 20% of all generated data. Enterprises must quickly sift through large amounts of data, much of which is, clearly, unstructured, to discover the data that will drive business choices. So, one might even be losing out on critical insights if the data analytics work is still limited to structured data. This is where unstructured data analysis is useful. Let’s take a better look at both unstructured and structured data and the data analytics step that follows.
Data – Structured and Unstructured
The data structure is a method of organizing and storing large amounts of data in a database or warehouse so that businesses can rapidly access and analyze it. The data in various formats can be divided into two categories: structured data and unstructured data (and sometimes including semi-structured data, too). While structured data can be used to characterize or identify behaviors, unstructured data can be used to provide a more detailed explanation, description, or prediction of a specific behavior or demand change.
Data that is provided in a fixed field within a file or record is referred to as structured data. So structured data refers to any information that is factually correct and well-organized. As it follows a pre-determined data model, it’s easy to analyze. Unstructured data, on the other hand, is information that lacks a preset data model or isn’t organized in a predetermined way. In simpler words, it’s any data that’s not structured, just like the name suggests. Although it does have an underlying structure, it isn’t structured in a prescribed fashion. There is no data model; the data is kept in its original format.

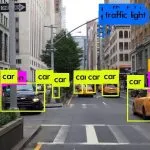
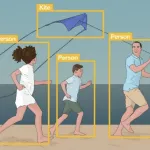
Structured data is stored in a relational database management system (RDBMS) and comes in the form of numbers and letters that fit exactly into the rows and columns of tables. Structured Query Language (SQL) is the computer language for structured data. Structured data is structured in a table with row and column relationships. Structured data is most commonly seen in Excel spreadsheets and SQL databases. In each of these, there are sorted rows and columns. Airline reservation systems, sales transactions, inventory control, and ATM activities are all examples of relational database applications using structured data. Unstructured data is typically text-based, but it can also include dates, figures, and facts. Unstructured data includes audio and video files, as well as No-SQL databases. Rich media, language, social media activity, and surveillance photography, among others, are all instances of unstructured data.
Also Read: The Ultimate Guide to the 4 Types of Data Analytics
Data Analytics – Structured and Unstructured
Apart from the apparent differences between keeping data in a relational database and outside of one, the most significant distinction between structured and unstructured data is the ease with which it may be analyzed. Structured data analytics is a well-established methodology and technology. Unstructured data analytics is a budding sector with a lot of new research and development investment, but it isn’t yet an established technology. Unstructured data analysis is the process of automatically organizing, structuring, and extracting value from unstructured data using data analytics technologies (information that is not organized in a pre-defined manner).
Unstructured data is more difficult to find, interpret, and understand than structured data. The lack of a predetermined model makes deconstructing unstructured data difficult.
We can’t use traditional numerical or statistical analytic methods to handle unstructured data since it doesn’t fit neatly into the row and column structure of a data table. Unstructured data presents numerous hurdles in terms of recognizing patterns, trends, and significance. So, how do we go about analyzing unstructured data? While unstructured data analysis procedures and technologies are still relatively new and fast-growing, recent advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence offer great promise in this area. Furthermore, unlike structured data, where various analytics tools are accessible for analysis, unstructured data has a limited number of analytics tools. For structured data, analytics tools do exist, but analytics tools for mining unstructured data are still in their infancy. Machine learning is used in unstructured data analytics technologies to collect and evaluate data that has no pre-defined framework, such as human language. Natural language processing (NLP) is a technique that allows the software to comprehend and evaluate text in the same way that a human would.
Combining Unstructured and Structured Data Analytics
The structured data vs. unstructured data debate in businesses is about deciding whether to invest in unstructured data analytics and whether it’s viable to combine the two for superior business information. While structured data analysis can help us understand what is going on, it is unstructured data that may indicate why. In the case of big data analytics, both structured and unstructured data must be integrated. Customer addresses and audio recordings might be mapped, or customer and sales automation data could be mapped to social media posts. However, there are obstacles when combining structured and unstructured data for extended data analysis, one of the most significant of them being the wide range of databases/ systems in which both types of data exist.


How Algoscale can help?
Businesses can start unveiling insights that were previously hidden behind massive volumes of unstructured data with the help of next-generation unstructured data analysis technologies. Algoscale is a leading data analytics firm in the United States, providing real-time monitoring, improved product delivery, and data-driven insights to help you transform your business and gain a competitive advantage. Harness the actual potential of your most precious asset, data, with our Data Analytics Solutions.